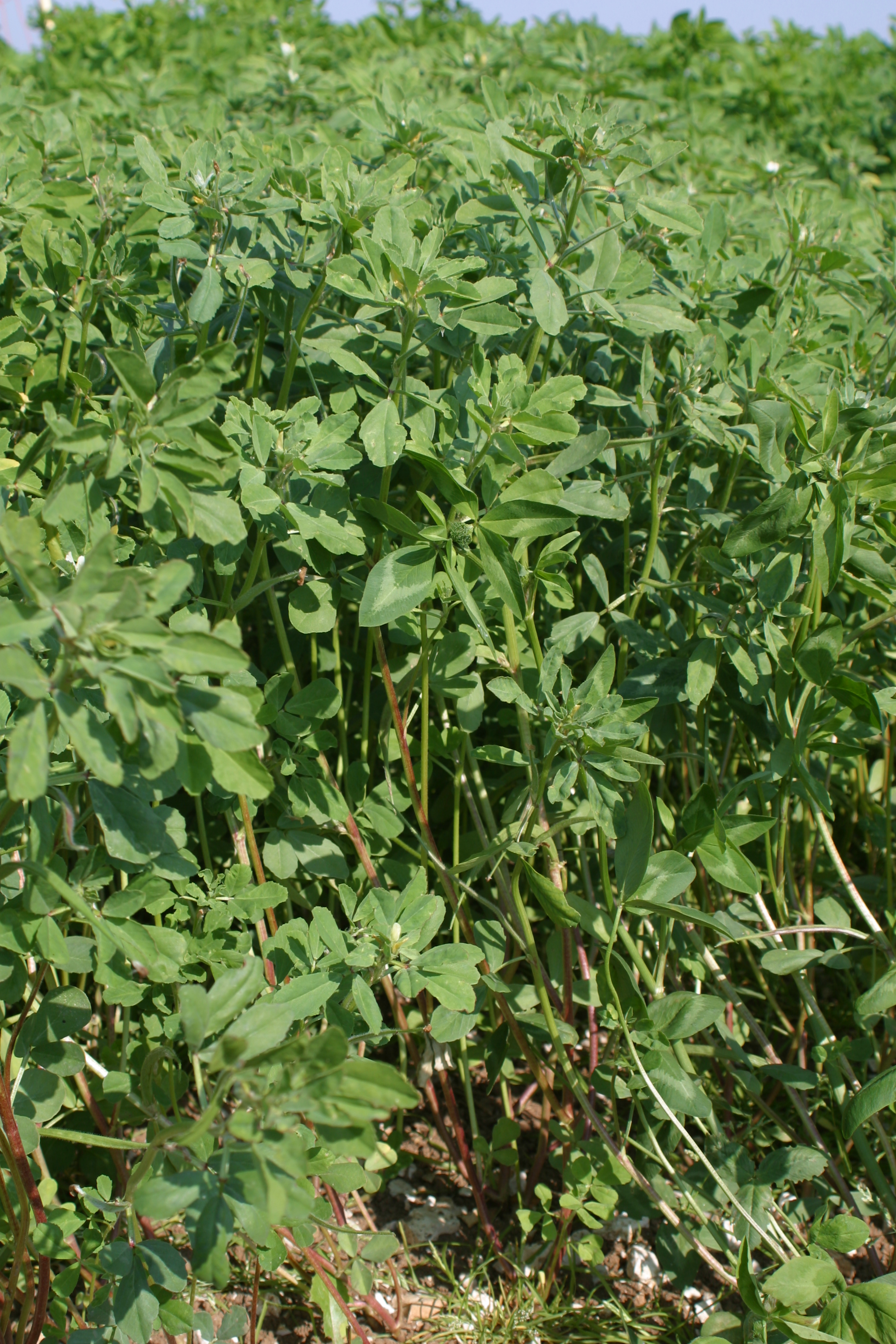
Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) is a legume. To reliably fix atmospheric nitrogen it should be mixed with the correct rhizobium meliloti to encourage nodulation.
Traditionally, the fenugreek plant has been used over the centuries as a herb and spice for cooking and medicinal purposes. In the UK there have been some trials carried out using the plant in polytunnels where productivity is high and gaps in rotation for fertility building are short. It is an easy to grow legume with good ground cover. Due to its rapid growth it will grow from seed to flowering and be ready to incorporate in 6 - 8 weeks.
Fenugreek grows best in light to medium free draining neutral soils,when handling the seed you will notice it has a distinct smell similar to cumin.
When to Sow: It should be planted into warm soils from mid to late spring, until mid summer. Autumn plantings are likely to succumb to early frost although this may differ in heated polytunnels.
Sowing Rate: 2.5 g/m2 - 10kg per acre - 25kg per ha,
Preparation: The most successful results come from sowing into a newly prepared seedbed. Aim to cultivate the top soil to about 5cm, with a light cultivator or discs. The finished seedbed should be fine but firm, with no clods. Several passes with a cultivator may be needed to achieve this.
Sowing: Seed should be broadcast or drilled to a shallow depth (not more than 1cm). Sowing too deep will reduce the germination dramatically. The soil should be rolled after sowing to increase seed to soil contact.
Management: Topping or mowing is not advised, unless prior to incorporation.
Date Posted: 20th January 2023