Hybrid Ryegrass
This form of ryegrass is perhaps one of the best grasses available to the intensive farmer. The hybrid ryegrass is a cross between the Italian and perennial forms of ryegrass and shares characteristics of both. The dominant parent determines how the variety performs in the field. Most hybrid varieties are dominant with Italian genes and the best cultivars provide the same or similar high yields as Italian ryegrass. But as they also contain some of the persistent genes of the perennial ryegrass parent they last longer. This longer lasting and high yielding silage grass has one further advantage: the genes of the perennial ryegrass parent produces a plant with more tillers and more leaf which gives increased ground cover, making them better for aftermath grazing.
Uses
Used for silage, haylage, hay and providing good aftermath grazing
Persistence
It will last for up to 4 years, yields can drop away sharply after this.
Strengths
This form of ryegrass is perhaps one of the best grasses available to the intensive farmer, offering high silage yields and grazing.
Frost Tolerance
Good frost tolerance
Yield
14t dry matter per ha
Sowing Rate Advice
14kg per acre / 35kg per ha
Ideal Sowing Time
Sow in the autumn for a full crop the following spring.
Management
Cutting for silage will depend on the heading date of the plant, each ryegrass species is different in terms of its maturity. Generally hybrid ryegrass will head around the 3rd week of May. As the plant starts to mature and develop a seed head the quality of the forage ( D-value) will decline. A D-value between 67-70 will provide good quality forage, which equates approximately to 25-50% ear emergence. When the plant is cut will depend on the type of stock the forage is to be fed to. Some stock require a lower quality, stemmier silage such as dry cows, while growing young stock require a higher quality forage. Hybrid ryegrass normally provides 2 full cuts on good ground. This species produces more leafy tillers from the base of the plant than Italian ryegrass., which means produces a better, less gappy grazing sward. Grazing the sward in mid to late autumn is important because it stops the crop going into the colder winter temperatures in a upright leafy state, where it can be affected by hard frosts. Grazing also allows the base of the sward to be cleaned out by the livestock and fresh growth encouraged early next spring. Hybrid ryegrass is susceptible to the usual pests and diseases found in ryegrass, including mildew and ryegrass mosaic virus. Modern varieties have good disease resistance scores, which can be found on the recommended list.
Distinguishing characteristics
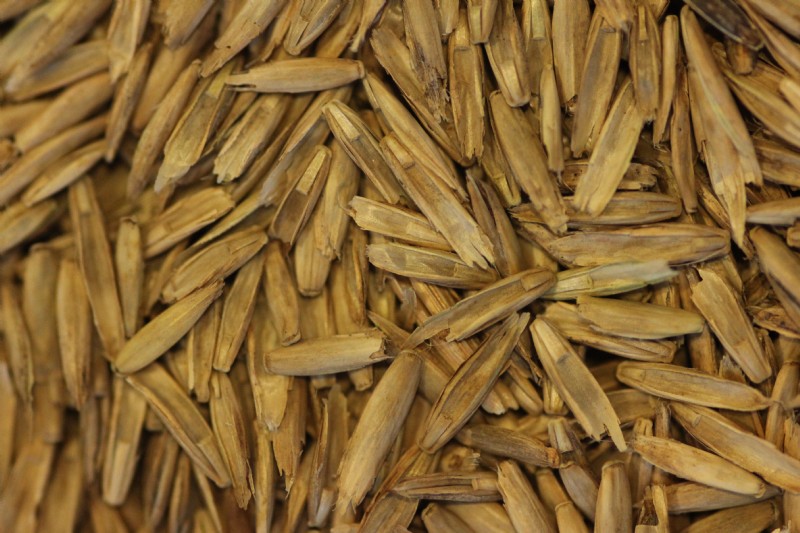
Seed
This seed has a narrowly, oblong shape. The seeds colour is beige, with a smooth papery texture. It is 5mm in length.
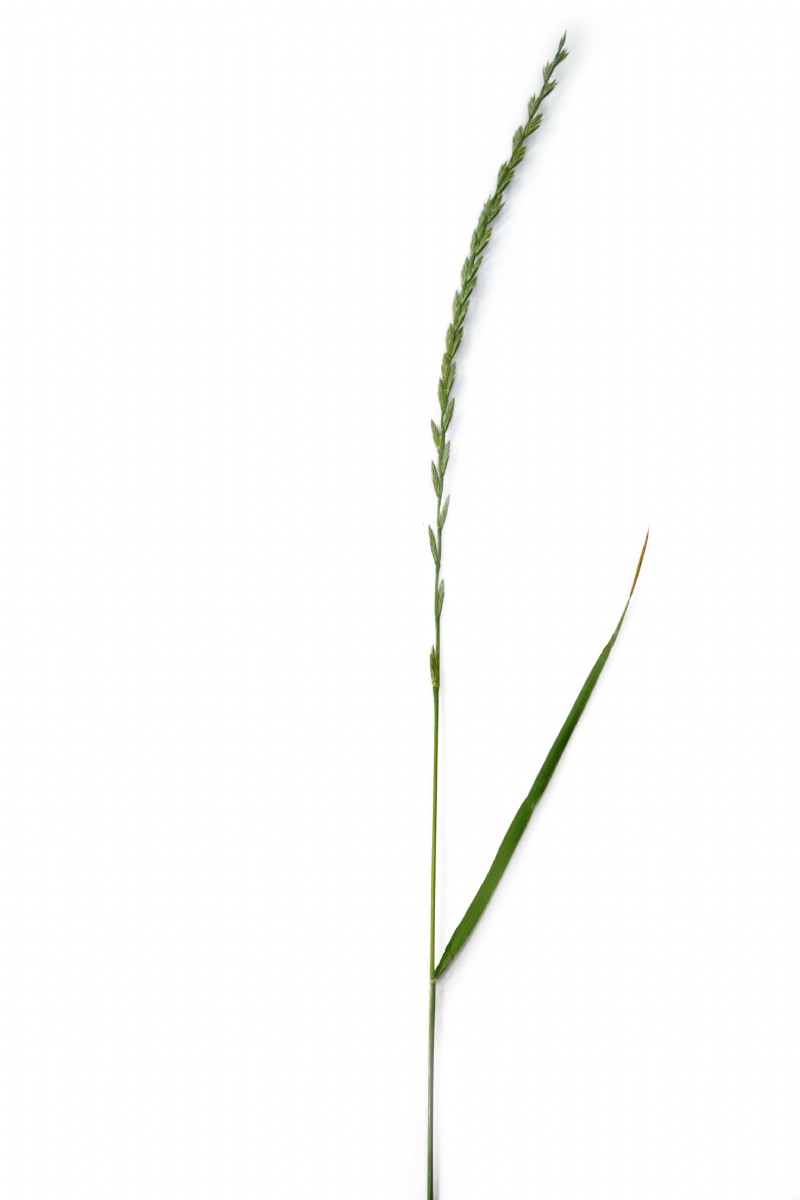
Flowering Plant
Glossy and dark green in colour, the leaves are smooth and shiny on the underside and slightly rougher on the top surface.
The species can vary due to the hybridisation between IRG and PRG.
The leaves can be up to 10 mm width.
Ligules vary from 1-2 mm.
As with other Ryegrass species, the distinctive inflorescence has spikelets arranged opposite each other along the axis.
Due to it hybridisation the spikelets can be awned or awnless.
It can reach from 30 - 90 cm in height
Additional Info
Flowers May - September Average seeds per kg - 400,000. Ryegrasses have high sugars and respond to nitrogen fertiliser better than any other grass species. These two qualities have made ryegrass the most popular grass for silage making for the last sixty years. Hybrid ryegrass generally heads around the 3rd week of May.
Works well with
The 4 year persistence of this species combines well with certain varieties of red clover, to produce a 3-4 year red clover and ryegrass lay.You can find Hybrid Ryegrass in the following mixtures
- Hybrid Silage Ley - Three-Four Year Ley
- Maximum D-Value Four-Five Year Silage Ley
- Hay & Graze - Four Year Dual Purpose Hay/Haylage Ley
- Hay & Graze Medium Term 4 year Hay Ley - 50% ORGANIC
- ‘POCHON’ Dairy Two-Four Year Silage/Grazing Ley
- ‘POCHON’ Dairy Two-Four Year Silage/Grazing 50% ORGANIC
- Intensive Dairy Graze - Early Four-Five Year Ley
- Early Bite Sheep & Hay Ley
- ‘CHOLDERTON’ Mix Four Year Plus Grazing/Cutting Ley
- ‘CHOLDERTON’ Mix Four Year Plus Grazing/Cutting Ley 50% ORGANIC
- Longer Term Red Clover 4 Year Ley
- Red Clover Ley Four Year Mixture 50% ORGANIC
- Ryegrass Over-Seeding Short Term 2-3 Years
- Ryegrass Over-Seeding Short Term 2-3 Years 50% ORGANIC
- Ryegrass Over-Seeding Longer Term 4-5 Years
- Ryegrass and Clover Over-Seeding Longer Term 4-5 Years
- Ryegrass Over-Seeding Longer Term 4-5 Years 50% ORGANIC
- Ryegrass & Clover Over-Seeding Longer Term 4-5 Yr 50% ORGANIC
- Drought Tolerant Over-Seeding Mixture 4-5 Year
- Drought Tolerant Over-Seeding Mixture 4-5 Year - 50% Organic
- Herbal Heavy Land Ley - for Medium and Clay Soil
- Herbal Heavy Land Ley - for Medium and Clay Soil - 50% ORGANIC
- ‘HERBAL’ Grazing Four Year Ley 50% ORGANIC
- Heavy Land Legume & Herb Rich Sward (OP4/SAM3) 70% Organic
- Simple Herbal Ley - 4 Year Grazing & Cutting Ley 50% ORGANIC
History
Breeding work in the 1960s and 1970s lead to the first successful hybridisation of the Italian and perennial ryegrass species, from 1996 onwards varieties began to be more commercially available and be entered on the recommended list.